Taste Buds: Location, Function & More! Discover Now
Is the very essence of flavor, that intricate dance of sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami, merely a matter of chemical reactions on our tongues? Absolutely. The perception of taste, a fundamental human experience, hinges on the remarkable structures known as taste buds, the gatekeepers of our gustatory world. These microscopic sentinels, nestled within the papillae of the tongue, are far more complex than we often give them credit for, and their function can be influenced by a surprisingly wide array of factors, from medications to overall health.The journey of taste begins when we ingest food or drink. As these substances come into contact with the tongue, their chemical components interact with specialized receptor cells located within the taste buds. These receptors, classified as chemoreceptors, are designed to detect specific molecules associated with each of the primary tastes. Once a receptor is activated, it triggers a cascade of events that ultimately lead to the transmission of a nerve impulse to the brain, where the sensation of taste is consciously perceived. However, this intricate process can be easily disrupted. Certain medications, such as antidepressants, are known to cause dry mouth, a condition that directly impacts the function of taste buds. Without adequate saliva, the chemical compounds in food cannot effectively reach the receptors, leading to a diminished or distorted sense of taste. Furthermore, various medical conditions and nutritional deficiencies can also interfere with the normal functioning of taste buds, resulting in altered taste perceptions.



| Taste Bud Function: A Comprehensive Overview | |
|---|---|
| Aspect | Details |
| Definition | Sensory receptor cells located on the tongue, responsible for detecting taste. |
| Location | Primarily on the tongue, within structures called papillae. Also found on the palate, pharynx, and epiglottis. |
| Structure | Each taste bud is an oval-shaped structure containing 50-100 receptor cells. These cells are surrounded by supporting cells and basal cells. |
| Types of Papillae |
|
| Taste Receptor Cells | Specialized cells that detect specific taste molecules. These cells have microvilli (hair-like projections) that extend into the taste pore, where they come into contact with saliva and food molecules. |
| Taste Sensations | Traditionally, five basic tastes are recognized:
|
| Chemoreception | Taste buds are classified as chemoreceptors because they detect chemical stimuli. |
| Mechanism of Action | When a taste molecule binds to a receptor on a taste receptor cell, it triggers a cascade of intracellular events that lead to the generation of an action potential. This electrical signal is then transmitted to the brain via sensory nerves. |
| Nerve Pathways | Taste information is transmitted to the brain via three cranial nerves:
|
| Brain Processing | Taste information is processed in several brain regions, including the gustatory cortex, which is responsible for the conscious perception of taste. |
| Factors Affecting Taste |
|
| Dry Mouth and Taste | Dry mouth, often caused by medications or medical conditions, reduces saliva production, which can lead to distortion of taste in the mouth. The taste buds close up, making it difficult for taste molecules to reach the receptors. |
| Vitamins and Supplements | Vitamins and other supplements are often a part of the dietary intake for supporting the bodys normal functioning, including the maintenance of healthy taste buds. |
| Research | Researchers at Louisiana State University have studied the nerve impulses coming from catfish taste buds, providing insights into the mechanisms of taste perception. Early research identified taste buds in fish. |
| Reference: National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) |
- Mark Wahlberg From Marky Mark To Hollywood Icon
- Uncensored Real Amateur Homemade Orgy Wife Sharing Nsfw
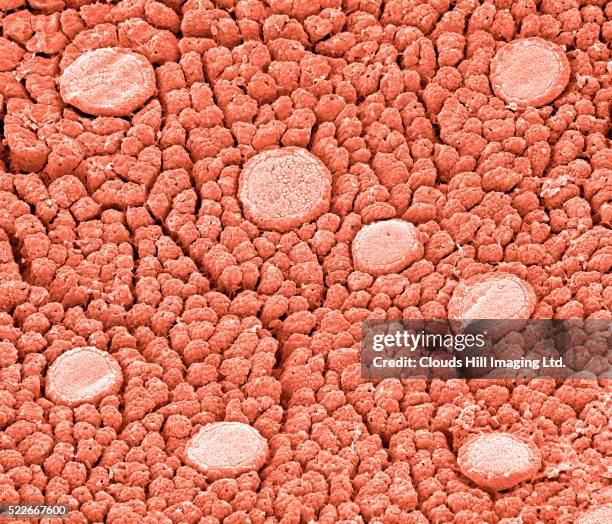
172 Taste Bud Closeup Stock Photos, High Res Pictures, and Images
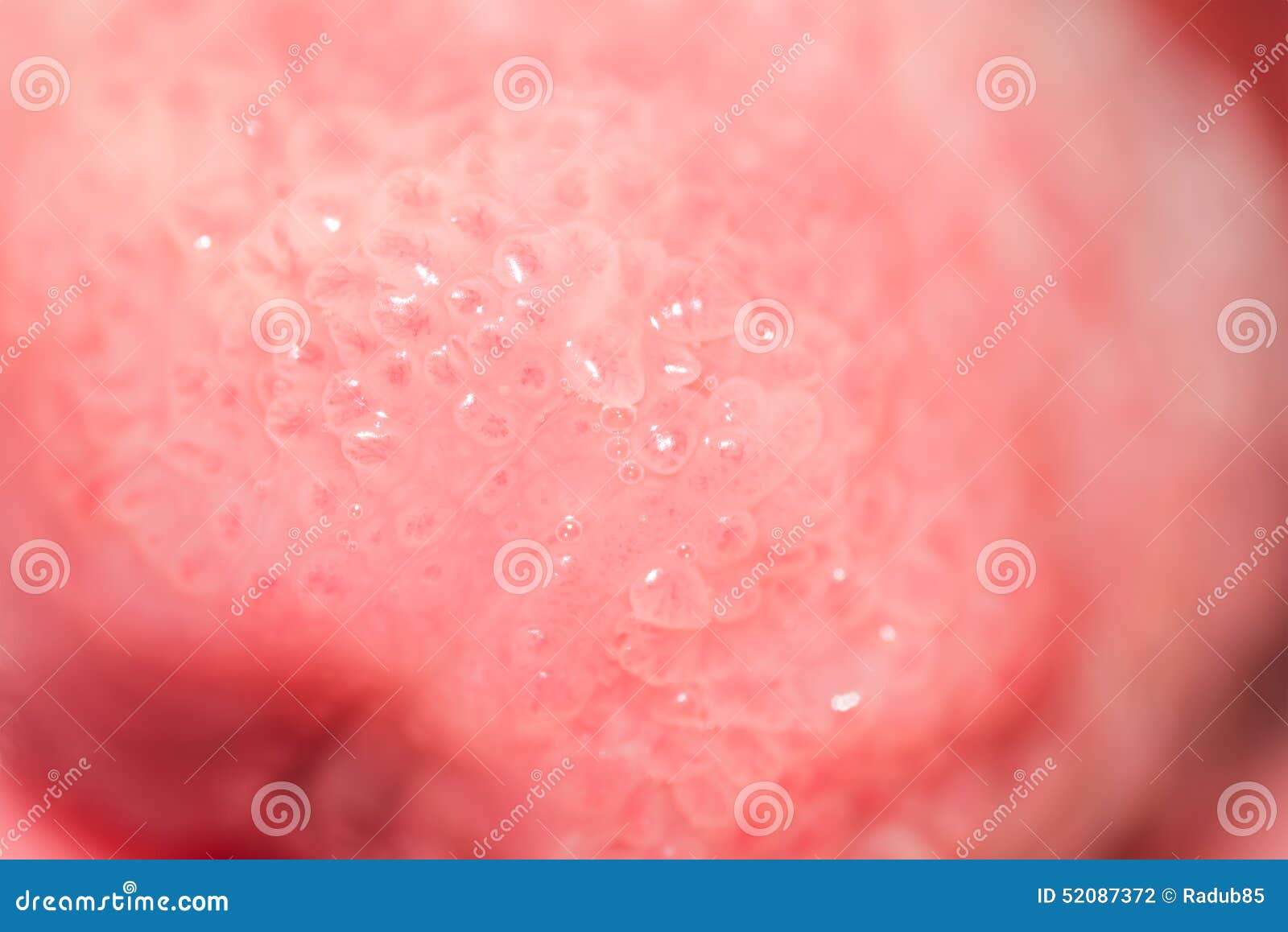
Taste Buds Close Up Spacotin
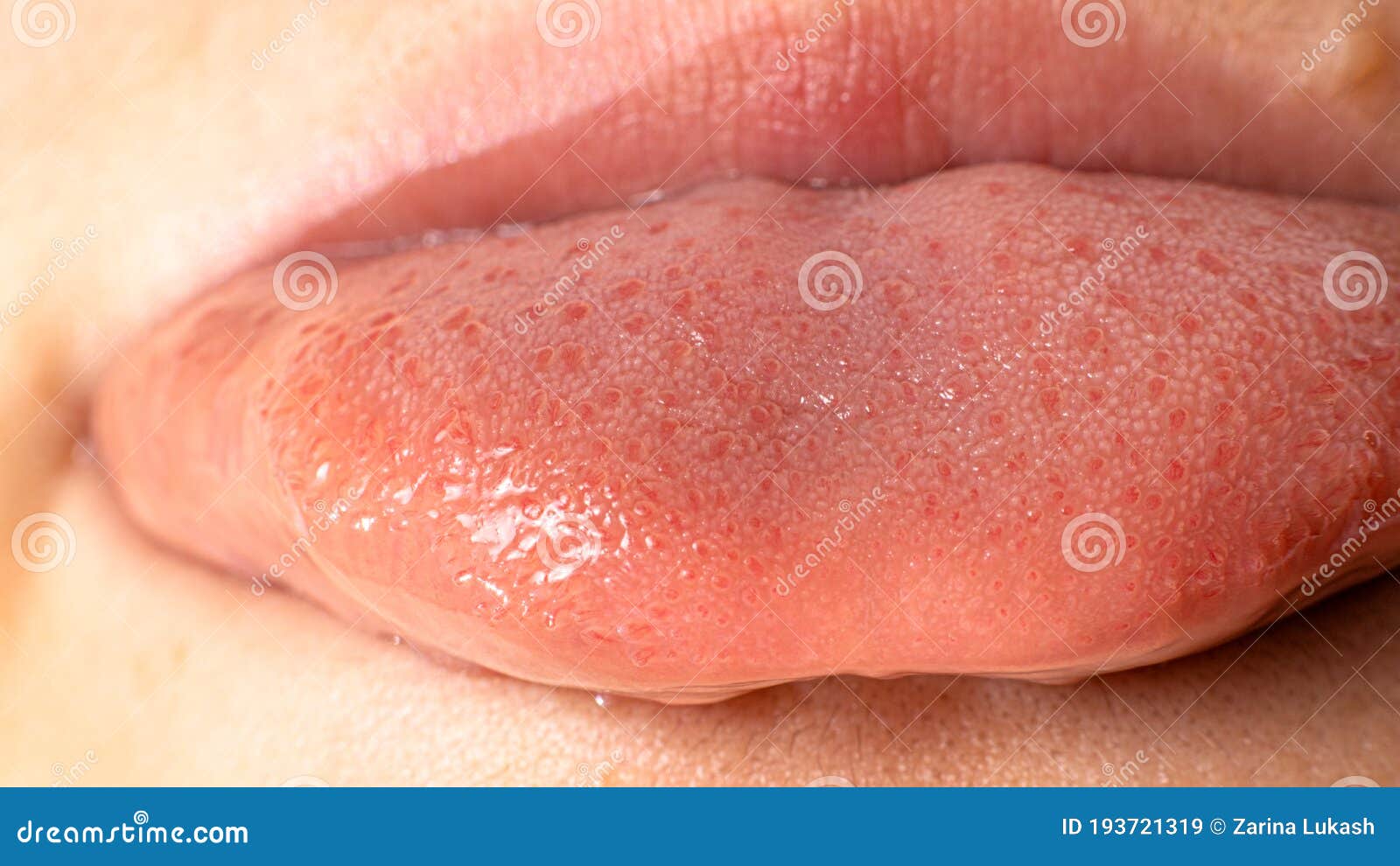
Macro Photo of Healthy Human Language. Tongue Papillae Taste Buds and